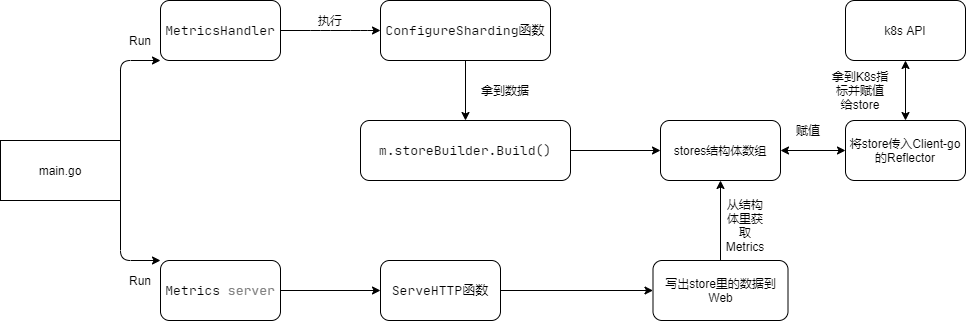
核心流程
在ksm的main中有三块启动服务的代码,我们只关注获得metrics的部分
//main.go 168行
// Run MetricsHandler
{
ctxMetricsHandler, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
g.Add(func() error {
return m.Run(ctxMetricsHandler)
}, func(error) {
cancel()
})
}
//main.go 188行
// Run Telemetry server
{
g.Add(func() error {
klog.Infof("Starting kube-state-metrics self metrics server: %s", telemetryListenAddress)
return web.ListenAndServe(&telemetryServer, tlsConfig, promLogger)
}, func(error) {
ctxShutDown, cancel := context.WithTimeout(ctx, 3*time.Second)
defer cancel()
telemetryServer.Shutdown(ctxShutDown)
})
}
//main.go 199行
// Run Metrics server
{
g.Add(func() error {
klog.Infof("Starting metrics server: %s", metricsServerListenAddress)
return web.ListenAndServe(&metricsServer, tlsConfig, promLogger)
}, func(error) {
ctxShutDown, cancel := context.WithTimeout(ctx, 3*time.Second)
defer cancel()
metricsServer.Shutdown(ctxShutDown)
})
}
其中暴露出/metrics接口的是第三块Run Metrics server部分的,他基于Go标准库启动了一个HTTP Server来通过Url方式暴露接口
其HTTP Server定义如下
// main.go 180行
telemetryMux := buildTelemetryServer(ksmMetricsRegistry)
telemetryListenAddress := net.JoinHostPort(opts.TelemetryHost, strconv.Itoa(opts.TelemetryPort))
telemetryServer := http.Server{Handler: telemetryMux, Addr: telemetryListenAddress}
metricsMux := buildMetricsServer(m, durationVec)
metricsServerListenAddress := net.JoinHostPort(opts.Host, strconv.Itoa(opts.Port))
metricsServer := http.Server{Handler: metricsMux, Addr: metricsServerListenAddress}
可以从buildMetricsServer中看到具体的HTTP接口定义
//main.go 48行
const (
metricsPath = "/metrics"
healthzPath = "/healthz"
)
//main.go 271行
func buildMetricsServer(m *metricshandler.MetricsHandler, durationObserver prometheus.ObserverVec) *http.ServeMux {
mux := http.NewServeMux()
// TODO: This doesn't belong into serveMetrics
mux.Handle("/debug/pprof/", http.HandlerFunc(pprof.Index))
mux.Handle("/debug/pprof/cmdline", http.HandlerFunc(pprof.Cmdline))
mux.Handle("/debug/pprof/profile", http.HandlerFunc(pprof.Profile))
mux.Handle("/debug/pprof/symbol", http.HandlerFunc(pprof.Symbol))
mux.Handle("/debug/pprof/trace", http.HandlerFunc(pprof.Trace))
mux.Handle(metricsPath, promhttp.InstrumentHandlerDuration(durationObserver, m))
// Add healthzPath
mux.HandleFunc(healthzPath, func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
w.Write([]byte(http.StatusText(http.StatusOK)))
})
// Add index
mux.HandleFunc("/", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.Write([]byte(`<html>
<head><title>Kube Metrics Server</title></head>
<body>
<h1>Kube Metrics</h1>
<ul>
<li><a href='` + metricsPath + `'>metrics</a></li>
<li><a href='` + healthzPath + `'>healthz</a></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>`))
})
return mux
}
其Metrics的关键在于mux.Handle(metricsPath,promhttp.InstrumentHandlerDuration(durationObserver, m))
//prometheus/promhttp/instrument_server.go 44行
// InstrumentHandlerDuration is a middleware that wraps the provided
// http.Handler to observe the request duration with the provided ObserverVec.
// The ObserverVec must have valid metric and label names and must have zero,
// one, or two non-const non-curried labels. For those, the only allowed label
// names are "code" and "method". The function panics otherwise. The Observe
// method of the Observer in the ObserverVec is called with the request duration
// in seconds. Partitioning happens by HTTP status code and/or HTTP method if
// the respective instance label names are present in the ObserverVec. For
// unpartitioned observations, use an ObserverVec with zero labels. Note that
// partitioning of Histograms is expensive and should be used judiciously.
//
// If the wrapped Handler does not set a status code, a status code of 200 is assumed.
//
// If the wrapped Handler panics, no values are reported.
//
// Note that this method is only guaranteed to never observe negative durations
// if used with Go1.9+.
func InstrumentHandlerDuration(obs prometheus.ObserverVec, next http.Handler) http.HandlerFunc {
code, method := checkLabels(obs)
if code {
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
now := time.Now()
d := newDelegator(w, nil)
next.ServeHTTP(d, r)
obs.With(labels(code, method, r.Method, d.Status())).Observe(time.Since(now).Seconds())
})
}
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
now := time.Now()
next.ServeHTTP(w, r)
obs.With(labels(code, method, r.Method, 0)).Observe(time.Since(now).Seconds())
})
}
从注释和代码都可以看见,这是一个Go HTTP Server的中间件Handler的实现,核心功能在于next.ServeHTTP
处,next是通过参数传入的
//main.go 162行
m := metricshandler.New(
opts,
kubeClient,
storeBuilder,
opts.EnableGZIPEncoding,
)
//pkg/metricshandler/metrics_handler.go 178行
// ServeHTTP implements the http.Handler interface. It writes the metrics in
// its stores to the response body.
func (m *MetricsHandler) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
m.mtx.RLock()
defer m.mtx.RUnlock()
resHeader := w.Header()
var writer io.Writer = w
resHeader.Set("Content-Type", `text/plain; version=`+"0.0.4")
if m.enableGZIPEncoding {
// Gzip response if requested. Taken from
// github.com/prometheus/client_golang/prometheus/promhttp.decorateWriter.
reqHeader := r.Header.Get("Accept-Encoding")
parts := strings.Split(reqHeader, ",")
for _, part := range parts {
part = strings.TrimSpace(part)
if part == "gzip" || strings.HasPrefix(part, "gzip;") {
writer = gzip.NewWriter(writer)
resHeader.Set("Content-Encoding", "gzip")
}
}
}
for _, s := range m.stores {
ms := s.(*metricsstore.MetricsStore)
ms.WriteAll(writer)
}
// In case we gzipped the response, we have to close the writer.
if closer, ok := writer.(io.Closer); ok {
closer.Close()
}
}
从注释就可知,/Metrics响应体就是通过这一块写,核心是下面这一块代码
for _, s := range m.stores {
ms := s.(*metricsstore.MetricsStore)
ms.WriteAll(writer)
}
//pkg/metrics_store/metrics_store.go 148行
// WriteAll writes all metrics of the store into the given writer, zipped with the
// help text of each metric family.
func (s *MetricsStore) WriteAll(w io.Writer) {
s.mutex.RLock()
defer s.mutex.RUnlock()
for i, help := range s.headers {
w.Write([]byte(help))
w.Write([]byte{'\n'})
for _, metricFamilies := range s.metrics {
w.Write(metricFamilies[i])
}
}
}
从上述代码可知,数据都是从m.stores里来的,这个来自ConfigureSharding这个函数调用中
//pkg/metricshandler/metrics_handler.go 69行
// ConfigureSharding (re-)configures sharding. Re-configuration can be done
// concurrently.
func (m *MetricsHandler) ConfigureSharding(ctx context.Context, shard int32, totalShards int) {
m.mtx.Lock()
defer m.mtx.Unlock()
if m.cancel != nil {
m.cancel()
}
if totalShards != 1 {
klog.Infof("configuring sharding of this instance to be shard index %d (zero-indexed) out of %d total shards", shard, totalShards)
}
ctx, m.cancel = context.WithCancel(ctx)
m.storeBuilder.WithSharding(shard, totalShards)
m.storeBuilder.WithContext(ctx)
m.stores = m.storeBuilder.Build()
m.curShard = shard
m.curTotalShards = totalShards
}
这个函数调用于
//pkg/metricshandler/metrics_handler.go 89行
// Run configures the MetricsHandler's sharding and if autosharding is enabled
// re-configures sharding on re-sharding events. Run should only be called
// once.
func (m *MetricsHandler) Run(ctx context.Context) error {
autoSharding := len(m.opts.Pod) > 0 && len(m.opts.Namespace) > 0
if !autoSharding {
klog.Info("Autosharding disabled")
m.ConfigureSharding(ctx, m.opts.Shard, m.opts.TotalShards)
<-ctx.Done()
return ctx.Err()
}
klog.Infof("Autosharding enabled with pod=%v pod_namespace=%v", m.opts.Pod, m.opts.Namespace)
klog.Infof("Auto detecting sharding settings.")
ss, err := detectStatefulSet(m.kubeClient, m.opts.Pod, m.opts.Namespace)
if err != nil {
return errors.Wrap(err, "detect StatefulSet")
}
statefulSetName := ss.Name
labelSelectorOptions := func(o *metav1.ListOptions) {
o.LabelSelector = fields.SelectorFromSet(ss.Labels).String()
}
i := cache.NewSharedIndexInformer(
cache.NewFilteredListWatchFromClient(m.kubeClient.AppsV1().RESTClient(), "statefulsets", m.opts.Namespace, labelSelectorOptions),
&appsv1.StatefulSet{}, 0, cache.Indexers{cache.NamespaceIndex: cache.MetaNamespaceIndexFunc},
)
i.AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: func(o interface{}) {
ss := o.(*appsv1.StatefulSet)
if ss.Name != statefulSetName {
return
}
shard, totalShards, err := shardingSettingsFromStatefulSet(ss, m.opts.Pod)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("detect sharding settings from StatefulSet: %v", err)
return
}
m.mtx.RLock()
shardingUnchanged := m.curShard == shard && m.curTotalShards == totalShards
m.mtx.RUnlock()
if shardingUnchanged {
return
}
m.ConfigureSharding(ctx, shard, totalShards)
},
UpdateFunc: func(oldo, curo interface{}) {
old := oldo.(*appsv1.StatefulSet)
cur := curo.(*appsv1.StatefulSet)
if cur.Name != statefulSetName {
return
}
if old.ResourceVersion == cur.ResourceVersion {
return
}
shard, totalShards, err := shardingSettingsFromStatefulSet(cur, m.opts.Pod)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("detect sharding settings from StatefulSet: %v", err)
return
}
m.mtx.RLock()
shardingUnchanged := m.curShard == shard && m.curTotalShards == totalShards
m.mtx.RUnlock()
if shardingUnchanged {
return
}
m.ConfigureSharding(ctx, shard, totalShards)
},
})
go i.Run(ctx.Done())
if !cache.WaitForCacheSync(ctx.Done(), i.HasSynced) {
return errors.New("waiting for informer cache to sync failed")
}
<-ctx.Done()
return ctx.Err()
}
而这个Run就是在上面一开始写过的Run MetricsHandler里面执行的
我们看m.stores = m.storeBuilder.Build()里面
// internal/store/builder.go 153行
// Build initializes and registers all enabled stores.
func (b *Builder) Build() []cache.Store {
if b.allowDenyList == nil {
panic("allowDenyList should not be nil")
}
stores := []cache.Store{}
activeStoreNames := []string{}
for _, c := range b.enabledResources {
constructor, ok := availableStores[c]
if ok {
store := constructor(b)
activeStoreNames = append(activeStoreNames, c)
stores = append(stores, store)
}
}
klog.Infof("Active resources: %s", strings.Join(activeStoreNames, ","))
return stores
}
其关键点在于constructor, ok := availableStores[c]这是在同一个文件下176行定义的一个map
var availableStores = map[string]func(f *Builder) cache.Store{
"certificatesigningrequests": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildCsrStore() },
"configmaps": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildConfigMapStore() },
"cronjobs": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildCronJobStore() },
"daemonsets": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildDaemonSetStore() },
"deployments": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildDeploymentStore() },
"endpoints": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildEndpointsStore() },
"horizontalpodautoscalers": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildHPAStore() },
"ingresses": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildIngressStore() },
"jobs": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildJobStore() },
"leases": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildLeases() },
"limitranges": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildLimitRangeStore() },
"mutatingwebhookconfigurations": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildMutatingWebhookConfigurationStore() },
"namespaces": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildNamespaceStore() },
"networkpolicies": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildNetworkPolicyStore() },
"nodes": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildNodeStore() },
"persistentvolumeclaims": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildPersistentVolumeClaimStore() },
"persistentvolumes": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildPersistentVolumeStore() },
"poddisruptionbudgets": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildPodDisruptionBudgetStore() },
"pods": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildPodStore() },
"replicasets": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildReplicaSetStore() },
"replicationcontrollers": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildReplicationControllerStore() },
"resourcequotas": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildResourceQuotaStore() },
"secrets": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildSecretStore() },
"services": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildServiceStore() },
"statefulsets": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildStatefulSetStore() },
"storageclasses": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildStorageClassStore() },
"validatingwebhookconfigurations": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildValidatingWebhookConfigurationStore() },
"volumeattachments": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildVolumeAttachmentStore() },
"verticalpodautoscalers": func(b *Builder) cache.Store { return b.buildVPAStore() },
}
因为Value里的函数定义了非常多,就不一一列举了,他们都是buildStore的多态实现
//internal/store/builder.go 337行
func (b *Builder) buildStore(
metricFamilies []generator.FamilyGenerator,
expectedType interface{},
listWatchFunc func(kubeClient clientset.Interface, ns string) cache.ListerWatcher,
) cache.Store {
metricFamilies = generator.FilterMetricFamilies(b.allowDenyList, metricFamilies)
composedMetricGenFuncs := generator.ComposeMetricGenFuncs(metricFamilies)
familyHeaders := generator.ExtractMetricFamilyHeaders(metricFamilies)
store := metricsstore.NewMetricsStore(
familyHeaders,
composedMetricGenFuncs,
)
b.reflectorPerNamespace(expectedType, store, listWatchFunc)
return store
}
这里边真正给store填充数据的,就是b.reflectorPerNamespace(expectedType, store, listWatchFunc)
这个函数将最终通过"k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache"下的cache.NewReflector把store传入k8s的reflector拿到最终数据
//internal/store/builder.go 355行
// reflectorPerNamespace creates a Kubernetes client-go reflector with the given
// listWatchFunc for each given namespace and registers it with the given store.
func (b *Builder) reflectorPerNamespace(
expectedType interface{},
store cache.Store,
listWatchFunc func(kubeClient clientset.Interface, ns string) cache.ListerWatcher,
) {
lwf := func(ns string) cache.ListerWatcher { return listWatchFunc(b.kubeClient, ns) }
lw := listwatch.MultiNamespaceListerWatcher(b.namespaces, nil, lwf)
instrumentedListWatch := watch.NewInstrumentedListerWatcher(lw, b.listWatchMetrics, reflect.TypeOf(expectedType).String())
reflector := cache.NewReflector(sharding.NewShardedListWatch(b.shard, b.totalShards, instrumentedListWatch), expectedType, store, 0)
go reflector.Run(b.ctx.Done())
}
这里只例举下核心函数,可以看见switch event.Type中对event类型进行判断,使用store自己的api来对store增删改查。
//k8s.io\client-go@v0.21.0\tools\cache\reflector.go 453行
// watchHandler watches w and keeps *resourceVersion up to date.
func (r *Reflector) watchHandler(start time.Time, w watch.Interface, resourceVersion *string, errc chan error, stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
eventCount := 0
// Stopping the watcher should be idempotent and if we return from this function there's no way
// we're coming back in with the same watch interface.
defer w.Stop()
loop:
for {
select {
case <-stopCh:
return errorStopRequested
case err := <-errc:
return err
case event, ok := <-w.ResultChan():
if !ok {
break loop
}
if event.Type == watch.Error {
return apierrors.FromObject(event.Object)
}
if r.expectedType != nil {
if e, a := r.expectedType, reflect.TypeOf(event.Object); e != a {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: expected type %v, but watch event object had type %v", r.name, e, a))
continue
}
}
if r.expectedGVK != nil {
if e, a := *r.expectedGVK, event.Object.GetObjectKind().GroupVersionKind(); e != a {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: expected gvk %v, but watch event object had gvk %v", r.name, e, a))
continue
}
}
meta, err := meta.Accessor(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", r.name, event))
continue
}
newResourceVersion := meta.GetResourceVersion()
switch event.Type {
case watch.Added:
err := r.store.Add(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to add watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Modified:
err := r.store.Update(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to update watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Deleted:
// TODO: Will any consumers need access to the "last known
// state", which is passed in event.Object? If so, may need
// to change this.
err := r.store.Delete(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to delete watch event object (%#v) from store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Bookmark:
// A `Bookmark` means watch has synced here, just update the resourceVersion
default:
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", r.name, event))
}
*resourceVersion = newResourceVersion
r.setLastSyncResourceVersion(newResourceVersion)
if rvu, ok := r.store.(ResourceVersionUpdater); ok {
rvu.UpdateResourceVersion(newResourceVersion)
}
eventCount++
}
}
watchDuration := r.clock.Since(start)
if watchDuration < 1*time.Second && eventCount == 0 {
return fmt.Errorf("very short watch: %s: Unexpected watch close - watch lasted less than a second and no items received", r.name)
}
klog.V(4).Infof("%s: Watch close - %v total %v items received", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, eventCount)
return nil
}
结论
从代码可知,关键就在于自身对store的实现,datadog-agent中也是对store和builder接口进行实现进行了自定义。
流程图